Micropile Applications:
- Supporting New Loads in Congested Areas
- Seismic Retrofit
- Arresting Structural Settlement
- Resisting Uplift/Dynamic Loads
- Underpinning
- Excavation Support in Confined Areas
- Reticulated Pile Wall
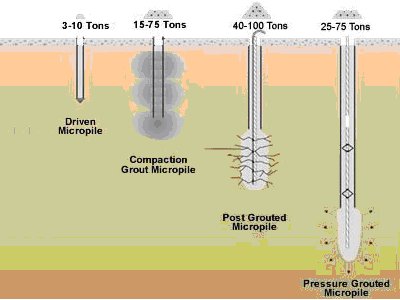
Types of Micropiles
- Pushed or Driven
- Compaction Grouted
- Post Grouted
- Pressure Grouted
Important Micropile Parameters
- Soil characteristics at pile shaft/soil
- interface Rock at pile tip
Benefits of Micropiles
- High-performance
- Design loads from 3 to 100+ tons
- Can be readily designed for tension/uplift loads
- Appropriate for a wide range of ground conditions
- Suitable for low headroom and restricted access
- Low noise and vibration
- Can penetrate obstacles
Micropile Design Steps
- Geotechnical study
- Determine load to be supported
- Design pile-to-structure connection
- Design pile-to-soil or rock load transfer
- Develop a pile testing program
Micropile Quality Control
Test selected piles to two times the static design load using standard ASTMD113 pile load test criteria
Typical Micropile Programs Involve
- Drilling holes, 2 inch to 12 inch diameter
- The construction of a pile shaft consisting of structural steel pipes, grout, steel sections and/or placement of reinforcing steel, as required by design
- The filling of the hole with high-strength cement grout
No comments:
Post a Comment